Time: 2025-02-13 13:48:00View:
FPGAs, Zynq, and Zynq MPSoC devices are all part of the programmable logic ecosystem, but they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics. Below is a detailed comparison of their features and use cases:
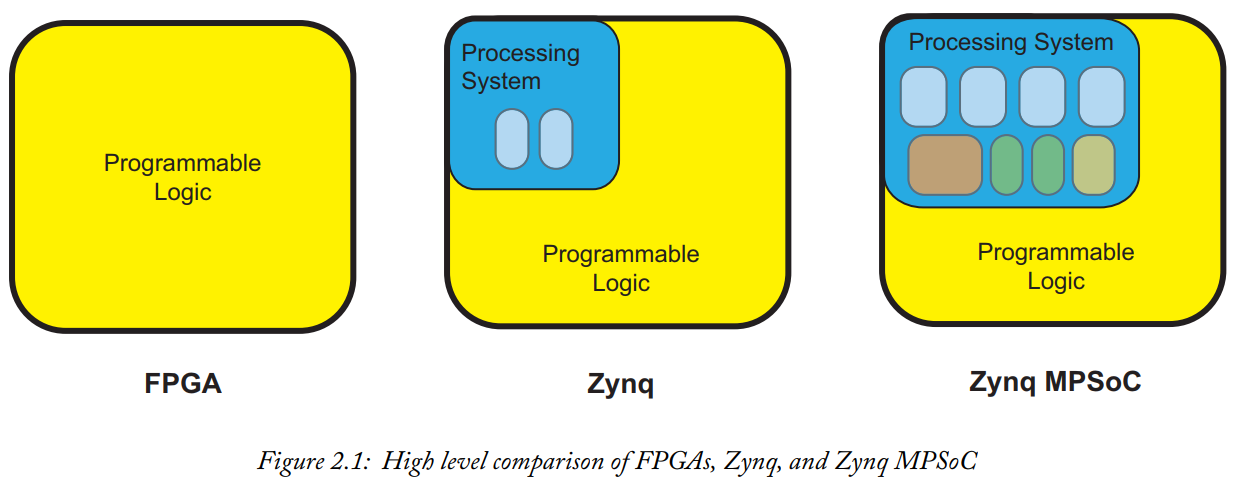
Programmable Logic: Composed of an array of configurable logic blocks (CLBs), DSP slices, block RAMs, and programmable interconnects.
Reconfigurability: Can be reprogrammed to implement different digital circuits.
No Built-in Processor: Requires an external processor (e.g., microcontroller or CPU) for software tasks.
High Parallelism: Excels at parallel processing, making it ideal for tasks like signal processing, cryptography, and custom hardware acceleration.
Flexibility: Can implement custom I/O interfaces and protocols.
Resource Types:
LUTs (Look-Up Tables): For logic implementation.
Flip-Flops (FFs): For sequential logic.
Block RAMs: For on-chip memory.
DSP Slices: For arithmetic operations.
Applications: ASIC prototyping, high-performance computing, real-time signal processing, and custom hardware design.
Hybrid Architecture: Combines an FPGA fabric with a dual-core ARM Cortex-A9 processor.
Processing System (PS):
Dual-core ARM Cortex-A9 CPU.
On-chip memory (DDR controller, cache).
Peripherals (Ethernet, USB, UART, GPIO).
Programmable Logic (PL):
FPGA fabric with LUTs, DSP slices, and block RAMs.
Hardware-Software Co-Design: Allows developers to partition tasks between the ARM processor (software) and the FPGA fabric (hardware).
Integrated Peripherals: Includes standard interfaces like Ethernet, USB, and HDMI, reducing the need for external components.
Reconfigurability: The FPGA fabric can be reprogrammed, while the ARM processor runs a fixed instruction set.
Applications: Embedded systems, IoT, robotics, industrial control, and multimedia.
Advanced Hybrid Architecture: Combines a more powerful processing system with a larger FPGA fabric.
Processing System (PS):
Quad-core ARM Cortex-A53 (application processing).
Dual-core ARM Cortex-R5 (real-time processing).
ARM Mali GPU (graphics processing).
On-chip memory (DDR controller, cache).
Advanced peripherals (PCIe, SATA, USB 3.0, DisplayPort).
Programmable Logic (PL):
Larger FPGA fabric with more LUTs, DSP slices, and block RAMs compared to Zynq-7000.
High Performance: Designed for more demanding applications, including AI, machine learning, and high-speed data processing.
Scalability: Available in different configurations to balance processing power and FPGA resources.
Security Features: Includes hardware security modules for secure boot and encryption.
Applications: AI/ML acceleration, 5G infrastructure, automotive systems, high-performance embedded computing.
| Feature | FPGA | Zynq-7000 | Zynq MPSoC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Processing Cores | None (external CPU required). | Dual-core ARM Cortex-A9. | Quad-core ARM Cortex-A53 + Dual-core Cortex-R5 + GPU. |
| FPGA Fabric | Yes (configurable logic blocks). | Yes (smaller fabric). | Yes (larger fabric). |
| Peripherals | Requires external interfacing. | Integrated (Ethernet, USB, HDMI). | Advanced (PCIe, SATA, USB 3.0, DisplayPort). |
| Reconfigurability | Fully reconfigurable. | FPGA fabric is reconfigurable. | FPGA fabric is reconfigurable. |
| Performance | High for parallel tasks. | Good for embedded systems. | High for complex applications. |
| Use Cases | Custom hardware, ASIC prototyping. | Embedded systems, IoT, robotics. | AI/ML, 5G, automotive, high-performance computing. |
| Complexity | Requires expertise in hardware design. | Easier for hardware-software co-design. | Suitable for advanced applications. |
| Cost | Varies (low to high depending on resources). | Moderate. | Higher (due to advanced features). |
FPGA: Best for custom hardware designs, high-performance computing, and applications requiring maximum flexibility.
Zynq-7000: Ideal for embedded systems that require both a processor and FPGA fabric, with integrated peripherals for ease of use.
Zynq MPSoC: Designed for advanced applications requiring high processing power, AI/ML acceleration, and complex system integration.
By understanding the characteristics of each device, you can choose the right platform for your project based on performance, complexity, and application requirements.